In the realm of accounting, reserves play a significant role in financial management and decision-making. Reserves are funds that are set aside for specific purposes, helping businesses address future contingencies and achieve their financial objectives. In this article, we will delve into the concept of reserves in accounting, exploring their importance, various types, and how they are utilized within an organization.

✅ AI Essay Writer ✅ AI Detector ✅ Plagchecker ✅ Paraphraser
✅ Summarizer ✅ Citation Generator
What are Reserves?
Reserves, in accounting, refer to profits that have been allocated for specific purposes rather than being distributed as dividends or utilized for share repurchases. These funds are safeguarded to ensure that they are available for designated uses, such as capital expenditures, legal settlements, debt repayment, bonuses, repairs, or maintenance.
Importance of Reserves
Ensuring Financial Stability
One key role of reserves is to promote financial stability within an organization. By setting aside funds for future obligations or investments, businesses can better manage unexpected events or economic downturns. Reserves act as a safety net, helping companies withstand unforeseen challenges without compromising their operational capabilities or long-term sustainability.
Signaling Financial Strength
The existence of reserves can signal financial strength to investors, creditors, and stakeholders. By demonstrating a commitment to allocate funds for specific purposes, businesses communicate their ability to meet future obligations and manage risks effectively. Reserves showcase prudent financial management and enhance the overall credibility and attractiveness of an organization.
Types of Reserves
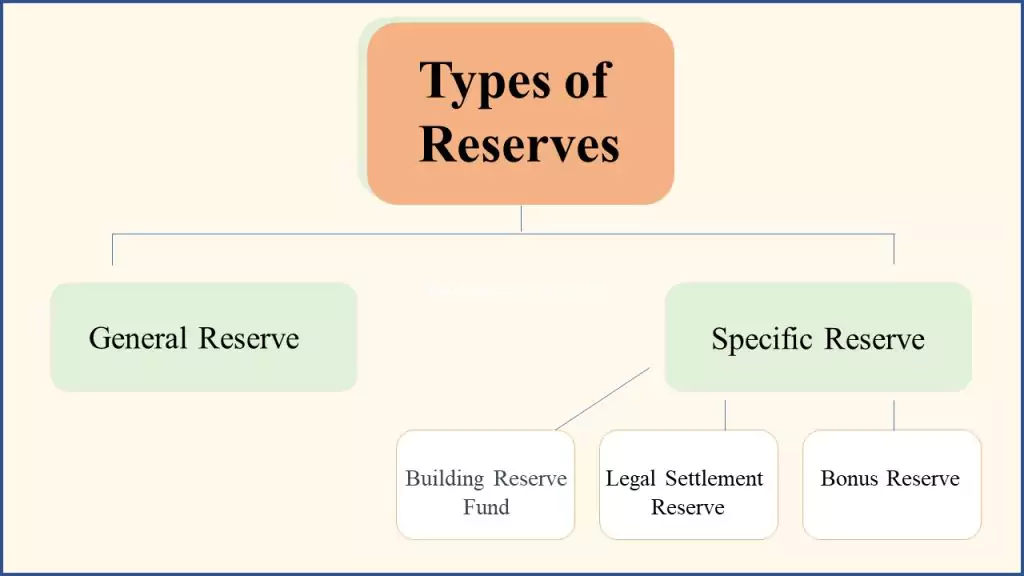
General Reserve
The general reserve, also known as the contingency reserve or revenue reserve, is a type of reserve that is not earmarked for any specific purpose. It serves as a buffer against unforeseen events and can be utilized to cover unexpected expenses or losses, ensuring business continuity. The general reserve provides flexibility and allows companies to navigate uncertainties more effectively.
Specific Reserves
Specific reserves are set aside for particular purposes or contingencies. They include various subcategories, each designated for a specific objective:
- Building Reserve Fund: This reserve is created to accumulate funds for future building construction projects. By allocating resources over time, businesses can ensure that they have the necessary capital to undertake significant infrastructure developments when needed.
- Legal Settlement Reserve: Companies may establish a reserve to cover potential legal settlements or disputes. These reserves help mitigate the financial impact of legal proceedings, ensuring that funds are available to address any legal obligations or liabilities that may arise.
- Bonus Reserve: Organizations often create a reserve to allocate funds for employee bonuses. This reserve ensures that bonuses can be paid without affecting the regular cash flow or hindering day-to-day operations.
Accounting for Reserves
To account for reserves, a simple journal entry is made. The retained earnings account is debited for the amount to be segregated, while the reserve account is credited for the same amount. This process effectively separates the funds from being used for other purposes.
Once the specific purpose or activity for which the reserve was created is completed, the initial entry is reversed. The reserve account is debited, and the retained earnings account is credited with the same amount, shifting the balance back to the retained earnings account.
Presentation of Reserves in Financial Statements
In financial statements, reserves can be presented separately as line items or aggregated into the retained earnings line item. The presentation approach depends on the organization’s reporting practices and the level of detail desired for the stakeholders.
Reserves are a crucial component of accounting, providing financial stability, flexibility, and signaling the strength of an organization. By setting aside funds for specific purposes, businesses can navigate uncertainties, meet future obligations, and make strategic investments. Whether it’s the general reserve or specific reserves like building, legal settlement, or bonus reserves, the appropriate allocation of funds strengthens a company’s financial position and instills confidence in stakeholders. Effective reserve accounting ensures that businesses have the resources to address contingencies and pursue long-term growth while safeguarding their financial well-being.
FAQ
What is the purpose of reserves?
The purpose of reserves is to set aside funds for specific purposes or contingencies, ensuring financial stability, addressing future obligations, and managing unexpected events or economic downturns.
Can reserves be used for any purpose?
While reserves are technically not legally restricted, they are typically designated for specific purposes outlined by the organization, such as capital expenditures, legal settlements, debt repayment, bonuses, or repairs. However, in practice, businesses usually adhere to the intended purpose of reserves.
What types of reserves are there in accounting? How do reserves impact financial statements?
In accounting, there are various types of reserves, including general reserves, specific reserves like building reserve funds, legal settlement reserves, and bonus reserves. Reserves can impact financial statements by providing a buffer against unforeseen events, demonstrating financial strength to stakeholders, and influencing the allocation of funds between retained earnings and designated reserves in the balance sheet.
Are reserves mandatory in accounting?
Reserves are not mandatory in accounting as there are no legal requirements for their establishment. However, businesses may choose to create reserves as a proactive financial management strategy to ensure the availability of funds for specific purposes and to enhance financial stability and credibility. The decision to establish reserves ultimately depends on the organization’s objectives and financial management practices.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.





Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.