Philosophy, often regarded as the pursuit of wisdom, has been a cornerstone of human intellectual endeavor for centuries. Throughout history, numerous philosophers have emerged as some of the greatest minds, shaping the course of human thought and influencing diverse areas of knowledge. In this article, we delve into the lives and contributions of the top 10 greatest philosophers, whose legacies continue to resonate in contemporary discourse.

✅ AI Essay Writer ✅ AI Detector ✅ Plagchecker ✅ Paraphraser
✅ Summarizer ✅ Citation Generator
Top 10 Greatest Philosophers in History
Studying philosophy is valuable for several reasons. Firstly, philosophy encourages critical thinking and rational inquiry. Moreover, philosophers grapple with fundamental questions about existence, morality, and knowledge, offering insights that challenge and broaden our perspectives. Understanding philosophical concepts equips individuals with a deeper understanding of the human condition and enhances their capacity for empathy and moral reasoning.
Socrates: The Socratic Method and Ethical Inquiry
Socrates, one of the most influential philosophers in history, laid the groundwork for Western philosophy through his dialectical method of inquiry, known as the Socratic method. By posing probing questions and engaging in dialogue, Socrates sought to uncover truth and expose contradictions in conventional wisdom. His emphasis on self-examination and moral introspection underscored the importance of ethical inquiry and self-knowledge in leading a virtuous life. His teachings continue to inspire philosophical discussions on ethics and epistemology to this day.
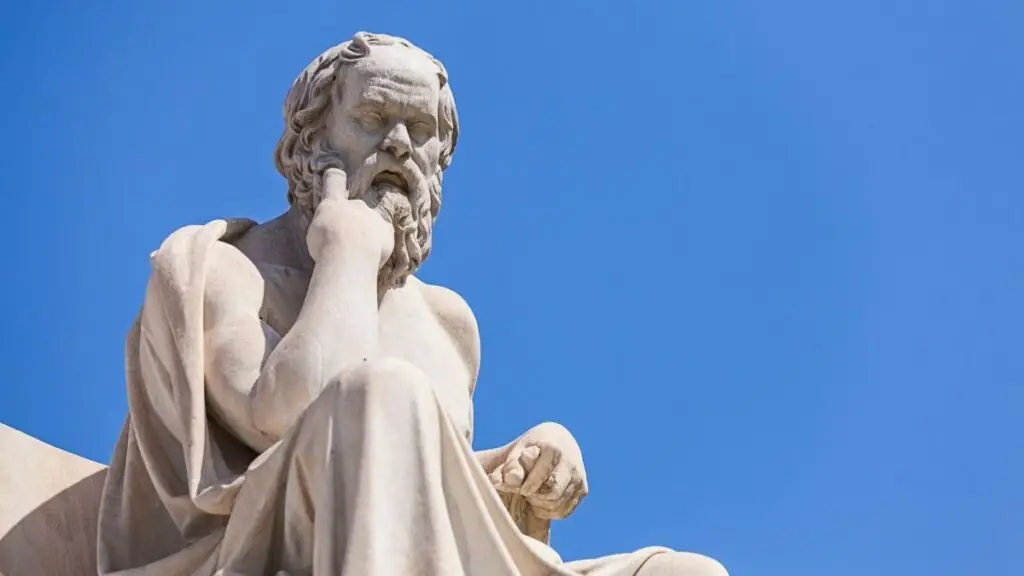

| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Socratic Method | Fundamental to Western Philosophy |
| Ethical Inquiry | Emphasis on self-examination and moral introspection |
| Virtue Ethics | Pursuit of virtuous life through knowledge and self-awareness |
Plato: Ideal Forms and The Republic
The pupil of Socrates, Plato, emerged as one of the preeminent philosophers of antiquity, renowned for his dialogues and profound insights into metaphysics, ethics, and politics. Plato’s theory of Forms posited the existence of ideal, eternal entities that serve as the ultimate reality behind the empirical world. In works like “The Republic,” Plato expounded upon his vision of the ideal state governed by philosopher-kings, advocating for justice, wisdom, and the pursuit of truth. His philosophical inquiries into justice, democracy, and the nature of reality remain influential in contemporary philosophical discourse, stimulating debates on governance, education, and the nature of knowledge.
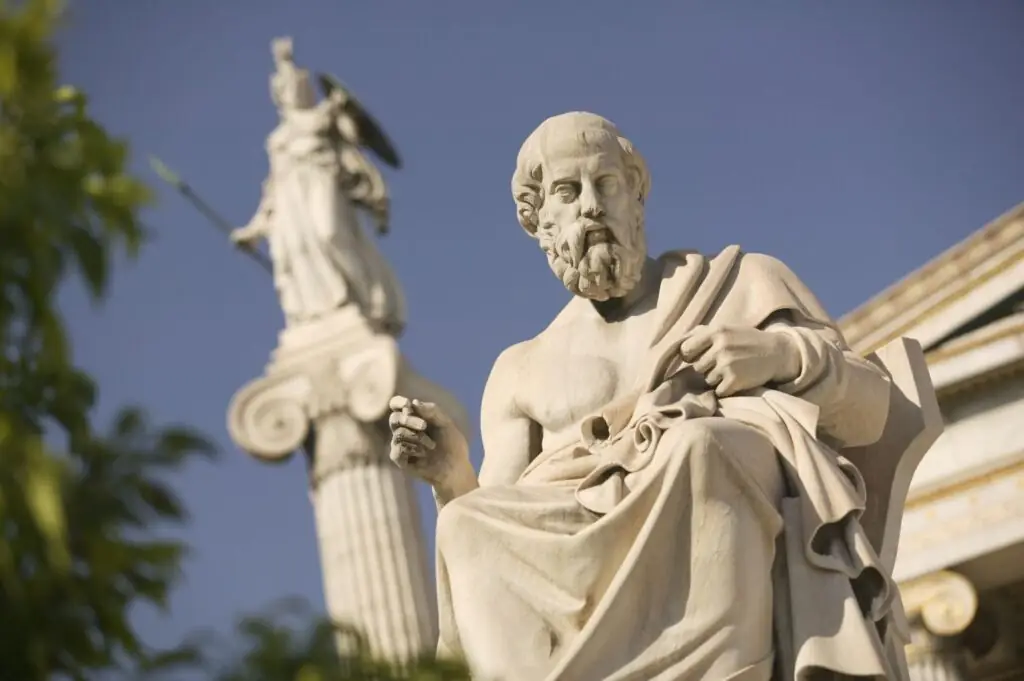

| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Theory of Forms | Concept of ideal, eternal entities |
| Philosopher-Kings | Ideal state governed by wisdom and justice |
| Allegory of the Cave | Enlightenment and education |
Aristotle: Logic, Ethics, and Natural Philosophy
Aristotle, a student of Plato and mentor to Alexander the Great, stands as one of history’s leading philosophers, contributing significantly to logic, ethics, and natural philosophy. His systematic approach to inquiry laid the groundwork for scientific methodology, while his ethical treatises, such as “Nicomachean Ethics,” explored the nature of virtue and the pursuit of eudaimonia, or human flourishing. Aristotle’s works encompassed diverse disciplines, shaping the intellectual landscape for centuries to come. His contributions to logic and biology laid the foundation for scientific inquiry, while his ethical theories continue to inform contemporary discussions on morality and the good life.
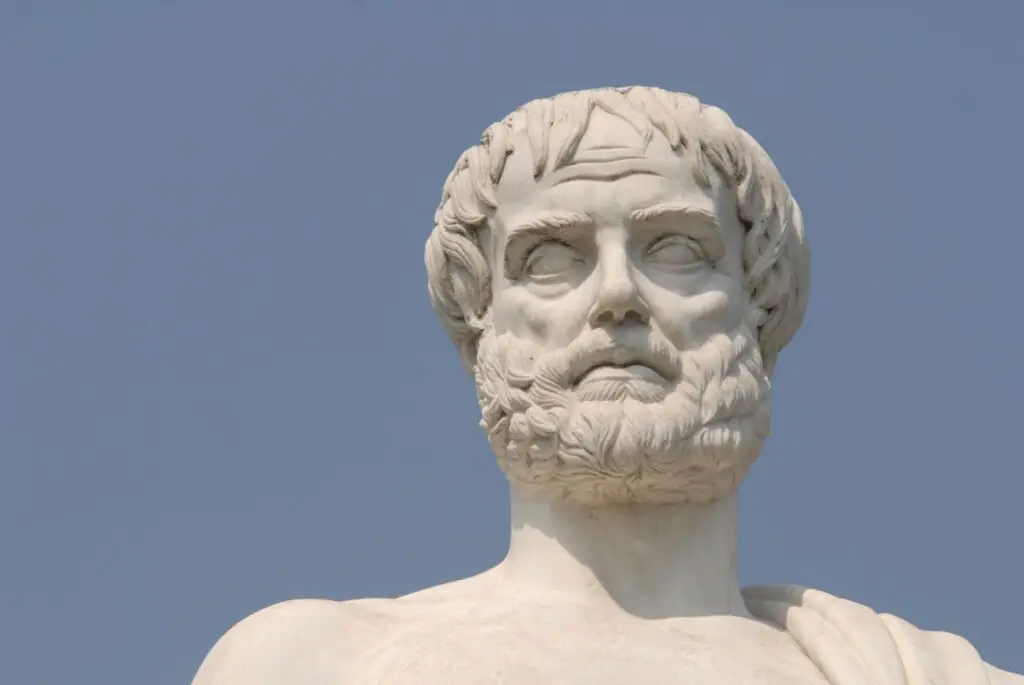

| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Logic | Foundational work in formal logic |
| Metaphysics | Exploration of being and reality |
| Virtue Ethics | Ethics grounded in moral virtues |
Confucius: Moral Principles and Social Harmony
In ancient China, Confucius emerged as a towering figure whose teachings profoundly influenced Chinese philosophy and culture. Emphasizing moral rectitude, filial piety, and social harmony, Confucius espoused a vision of ethical conduct grounded in the cultivation of moral virtues and the fulfillment of social roles. His philosophy emphasized the importance of education, self-cultivation, and the cultivation of moral character in fostering a harmonious society. Confucian principles continue to shape East Asian societies, informing social norms, educational practices, and ethical values, highlighting the enduring relevance of his teachings in contemporary contexts.
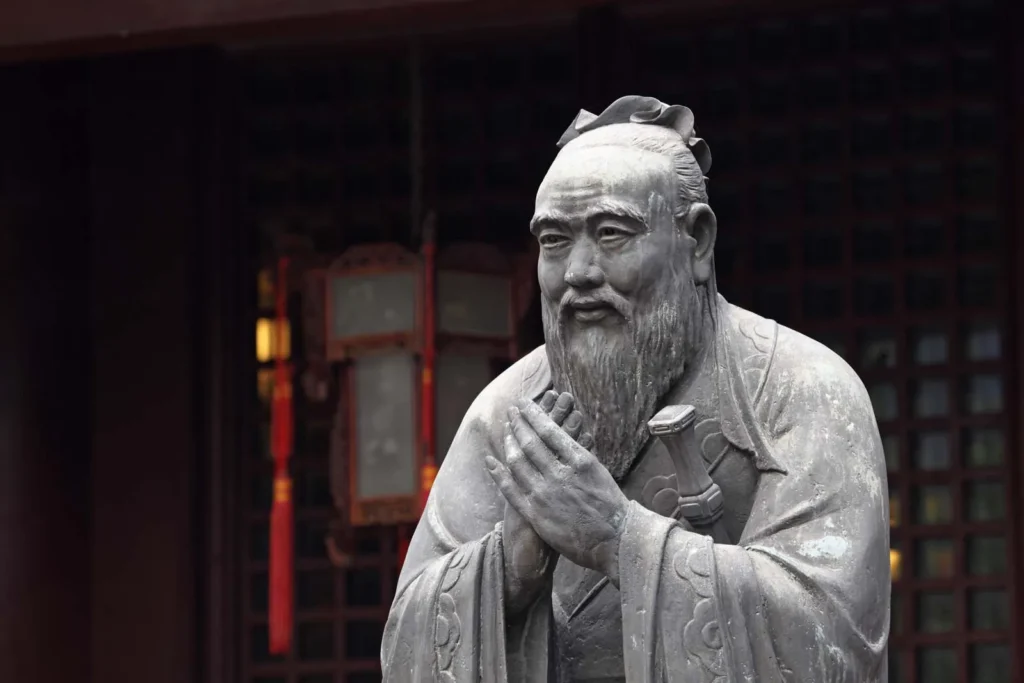

| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Confucianism | Ethical and social philosophy |
| Five Relationships | Foundation for social harmony |
| Golden Rule | Moral principle of reciprocity |
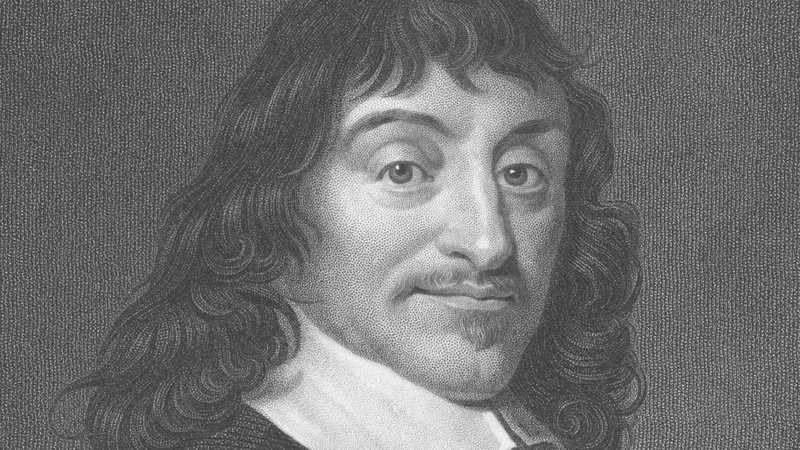
René Descartes: Cartesian Dualism and Rationalism
René Descartes, often hailed as the father of modern philosophy, revolutionized the landscape of thought with his method of doubt and emphasis on rationalism. Through his famous dictum, “Cogito, ergo sum” (I think, therefore I am), Descartes laid the foundation for his epistemological project, seeking to establish indubitable truths through the power of reason. His dualistic framework, which posited the existence of mind and matter as distinct substances, profoundly influenced subsequent philosophical inquiry. Descartes’ methodological skepticism and emphasis on rational inquiry continue to shape contemporary discussions in epistemology, metaphysics, and the philosophy of mind.

| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Method of Doubt | Systematic skepticism |
| Cartesian Dualism | Mind-body distinction |
| Cogito, ergo sum | Existential certainty |
Immanuel Kant: Critique of Pure Reason and Moral Philosophy
Immanuel Kant, a towering figure of the Enlightenment, took on a project to reconcile empiricism and rationalism while revolutionizing moral philosophy. In his monumental work, “Critique of Pure Reason,” Kant sought to delineate the limits of human knowledge and establish the principles of metaphysics grounded in the faculties of the mind. Additionally, his moral philosophy, articulated in works like the “Groundwork of the Metaphysics of Morals,” highlighting the autonomy of the moral agent and the categorical imperative as the supreme principle of morality. Kant’s contributions to epistemology, ethics, and metaphysics continue to influence contemporary philosophical debates on knowledge, morality, and the nature of reality.

| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Categorical Imperative | Moral principle of universalizability |
| Critique of Pure Reason | Limits of human knowledge |
| Transcendental Idealism | Epistemological framework |
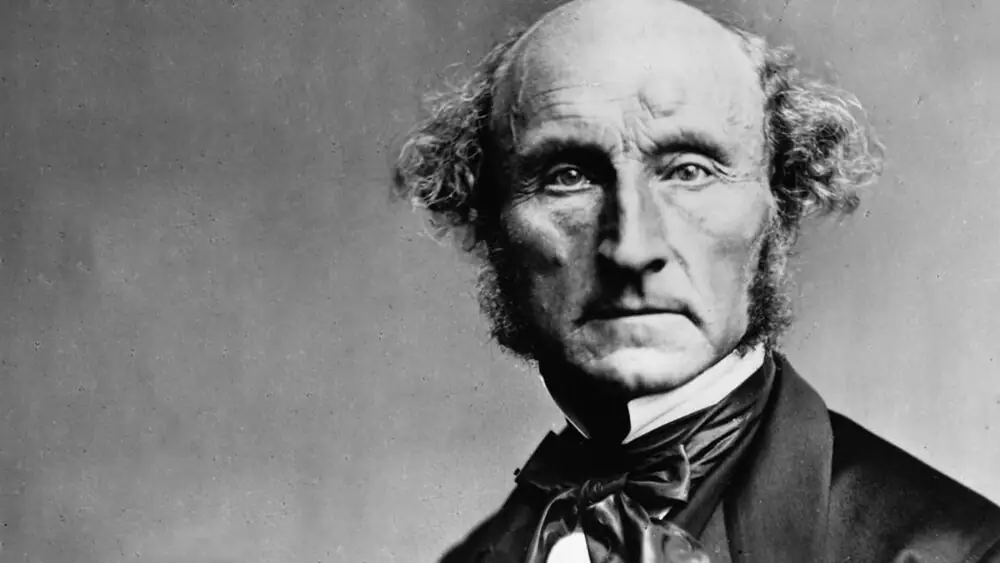
John Stuart Mill: Utilitarianism and Liberalism
John Stuart Mill, an influential figure in 19th-century philosophy and political thought, championed the principles of utilitarianism and liberalism. In his seminal work, “Utilitarianism,” Mill advocated for the greatest happiness principle as the foundation of morality, positing that actions should be judged by their tendency to promote the overall well-being of sentient beings. Furthermore, his defense of individual liberty and freedom of expression in works like “On Liberty” continues to shape contemporary debates on civil liberties and human rights. Mill’s advocacy for utilitarian ethics and liberal principles has had a lasting impact on ethical theory and political philosophy, informing discussions on social justice, democracy, and individual autonomy.

| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Utilitarianism | Greatest happiness principle |
| On Liberty | Defense of individual liberty |
| Harm Principle | Principle of personal freedom |
Friedrich Nietzsche: Will to Power and Existentialism
Friedrich Nietzsche, a provocative and controversial figure in philosophy, critiqued traditional morality and championed individualism and self-overcoming. In works like “Thus Spoke Zarathustra” and “Beyond Good and Evil,” Nietzsche challenged conventional notions of morality and religion, advocating for the affirmation of life’s inherent complexities and contradictions. His concept of the will to power and critique of nihilism laid the groundwork for existentialist thought and influenced a wide range of philosophical and literary movements. Nietzsche’s exploration of existential themes and his critique of traditional values continue to resonate in contemporary discussions on morality, meaning, and human nature.
| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Will to Power | Driving force of human existence |
| Ubermensch | Ideal of self-overcoming |
| Critique of Morality | Rejection of traditional values |
Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir: Existentialism and Feminist Philosophy
Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir, prominent figures in existentialist philosophy, explored themes of freedom, authenticity, and responsibility in their works. Sartre’s existentialist manifesto, “Being and Nothingness,” examined the nature of consciousness and the individual’s struggle to define their existence in a seemingly indifferent universe.
| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Existentialism | Emphasis on individual freedom |
| Existence Precedes Essence | Subjectivity and personal responsibility |
| Bad Faith | Self-deception and inauthenticity |

Meanwhile, Beauvoir’s groundbreaking work, “The Second Sex,” laid the foundation for feminist existentialism, critiquing the social construction of gender and advocating for women’s liberation and autonomy. Their contributions to existentialist philosophy and feminist theory have had a profound impact on contemporary discussions of identity, power, and liberation.
| Main Teachings | Contributions |
|---|---|
| The Second Sex | Feminist critique of patriarchal society |
| Existential Feminism | Women’s liberation and autonomy |
| Ethics of Ambiguity | Embrace of existential freedom |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the top 10 greatest philosophers have left an indelible mark on human thought, shaping intellectual discourse and challenging conventional wisdom throughout history. From ancient Greece to the modern era, these influential thinkers have illuminated the human condition, offering profound insights into the nature of reality, morality, and existence.
FAQ
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.





Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.