When launching academic research, one question often looms large in the minds of many: “How long is a proper dissertation?” This seemingly simple query holds within its layers of complexity, much like the dissertation itself. The question is not about the number of pages – it’s about the depth of analysis, the strength of the argument, and the breadth of the literature review.

✅ AI Essay Writer ✅ AI Detector ✅ Plagchecker ✅ Paraphraser
✅ Summarizer ✅ Citation Generator
Key Takeaways:
- The length of a dissertation is influenced by plenty of factors, including the type of research, the academic discipline, and specific institutional guidelines.
- A dissertation comprises various sections, from the abstract to the references. Understanding the typical length and depth of each component can clarify the dissertation’s overall length and structure.
- The time required to write a dissertation can range from a few months for master’s students to several years for doctoral candidates.
- While understanding average lengths and durations is helpful, the emphasis should always be on the quality of research and writing.
In the kingdom of academic writing, a dissertation proudly wears the crown. It is the queen – the most important, the most intricate, and, of course, the most time-consuming written work. From the abstract to the conclusion, from the glossary to the acknowledgments, every chapter and heading demands painstaking attention. With such a significant requirement, it’s natural to wonder how many pages a future Ph.D. holder should be prepared to write. How does the institution or the supervisor influence the formatting and length? What role does the research process play in determining the body of the work? And can the paper be turned down if it’s shorter than some existing standard?
Fear not, for this article is here to guide you through the complexities of dissertation length, offering insights, references, and clarity on this pivotal aspect of your academic journey. Whether you’re just starting out or are deep into your thesis, understanding the length and structure will undoubtedly help in your academic success. For additional support, students should take a look at the top 10 dissertation writing services to make writing a dissertation a breeze.
Types of Dissertations
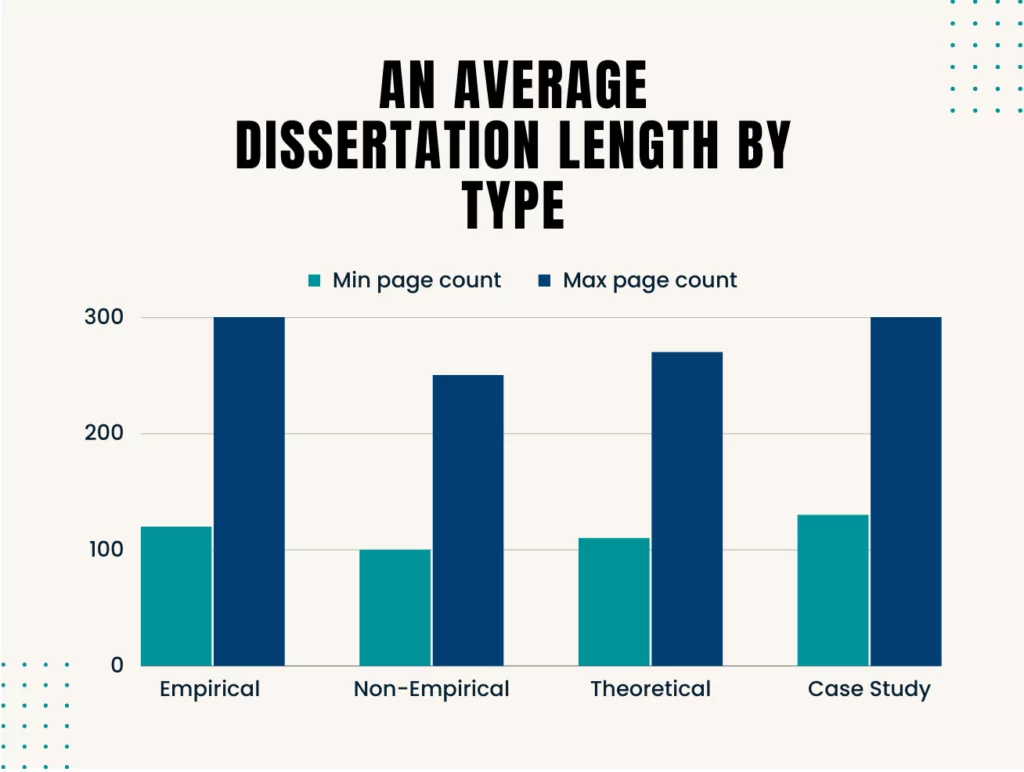
Much like the vast fields of research they encompass, dissertations come in various shapes and sizes. The length of a dissertation can vary based on several factors, including the type of research, the discipline, the institution’s requirements, and the depth of analysis. Let’s explore the different types of dissertations and their average lengths.
Length of Dissertations Based on Research
Empirical Dissertations
These involve collecting data from the real world. This could be through observations, surveys, or experiments. Due to the need for detailed data presentation and analysis, empirical dissertations tend to be longer.
| Data Collection | This type of dissertation requires the researcher to go into the field, whether it’s conducting interviews, distributing surveys, or performing experiments. |
| Methodology | The methodology section is crucial, detailing how the data was collected and why specific methods were chosen. |
| Analysis | Once data is collected, it’s subjected to rigorous analysis, often using statistical tools, to draw meaningful conclusions. |
EXAMPLE:
A psychology researcher decides to study the impact of mindfulness meditation on stress levels among college students. They design an experiment where one group of students practices mindfulness meditation for 20 minutes daily, while a control group does not. Over a semester, the researcher collects data on stress indicators, such as cortisol levels and self-reported stress scales.
- Average Page Count: Given the need to detail the methodology, present raw data, and provide a comprehensive analysis, empirical dissertations tend to be lengthier. They often range from 120 to 300 pages, depending on the depth and breadth of the data collected.
Non-Empirical Dissertations
Non-empirical dissertations are based on existing data or literature. Instead of collecting new data, researchers analyze what’s already available to make a new argument or perspective.
| Literature Review | This is the heart of a non-empirical dissertation. Researchers spend significant time reviewing existing literature to identify gaps or new angles of exploration. |
| Argumentation | The focus is on building a strong argument or perspective based on the existing literature. |
| Critical Analysis | Researchers critically analyze previous studies, theories, or data to support their thesis. |
EXAMPLE:
A literature scholar chooses to analyze the representation of nature in the works of William Wordsworth. Instead of collecting new data, the researcher explores Wordsworth’s poems, existing critiques, and historical contexts to build a nuanced argument about the poet’s unique perspective on nature.
- Average Page Count: Since non-empirical dissertations rely heavily on existing literature and critical analysis, they may be shorter than empirical ones but still comprehensive. They typically range from 100 to 250 pages.
Theoretical Dissertations
These focus on developing new theories or analyzing existing ones. Their length can vary widely based on the complexity of the theory, but they may reach up to 270 pages.
| Conceptual Exploration | The researcher delves deep into concepts, exploring and challenging existing theoretical frameworks. |
| Model Building | These dissertations are more abstract and less concrete, focusing on ideas and concepts rather than measurable data. |
| Abstract Analysis | A dissertation proposing a new theory of social interaction or a study examining the limitations of a current economic model. |
EXAMPLE:
A philosophy student is intrigued by the concept of free will. They decide to develop a new theoretical framework that reconciles free will with determinism. The dissertation delves into existing theories, identifies gaps or contradictions, and proposes a new model of understanding free will.
- Average Page Count: Theoretical dissertations can vary widely based on the complexity of the theory and the depth of exploration. However, given the emphasis on conceptual exploration and model building, they generally range from 110 to 270 pages.
Case Study Dissertations
Case study dissertations focus on an in-depth analysis of a specific case, event, individual, or context. They provide detailed insights into real-world situations.
| Deep Dive | Researchers spend significant time understanding the nuances of a particular case, often using multiple sources of data. |
| Contextual Analysis | The focus is on understanding the case within its broader context, drawing insights that might be applicable elsewhere. |
| Multiple Perspectives | Often, case studies will consider various perspectives to provide a holistic view of the situation. |
EXAMPLE:
A business student is interested in understanding the success of a local startup that has recently gained significant market share. They conduct in-depth interviews with the company’s founders, employees, and customers, analyze its marketing and financial strategies, and compare it with competitors to draw insights.
- Average Page Count: Due to their detailed nature, case study dissertations can be quite extensive. They often range from 130 to 300 pages, depending on the depth of the case and the number of data sources analyzed.
How Long Should a Dissertation Be?
Diverse factors influence the length of dissertations. While the type of work—be it empirical, theoretical, or case study—plays an essential role in determining its size, another equally significant determinant is the academic discipline itself. Each field of knowledge has its unique traditions, methodologies, and expectations. These difficulties often dictate the depth of research, the paper’s structure, and its length. As we explore the various disciplines and their respective characteristics, let’s examine how average dissertation length varies.
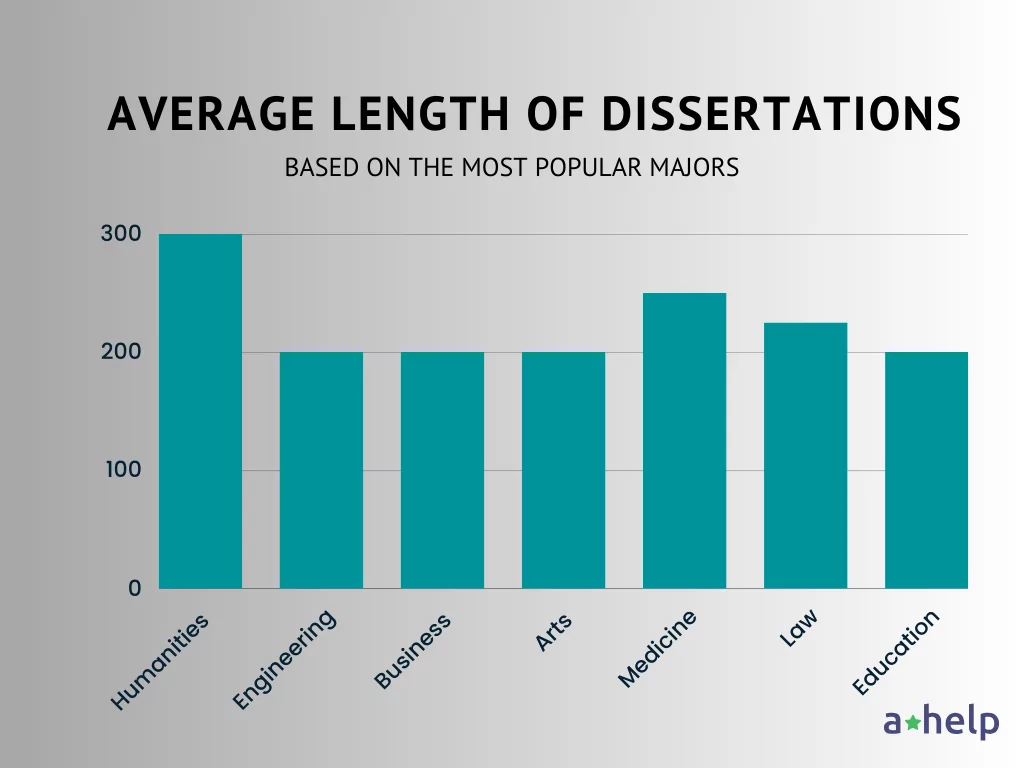
Humanities and Social Sciences
In disciplines like history, philosophy, sociology, and literature, the dissertation often involves a deep investigation of theoretical frameworks and extensive literature reviews. Given the need for comprehensive analysis and the inclusion of various perspectives, dissertations in these fields can be quite lengthy. They often range from 200 to 400 pages, with some even exceeding this range for exceptionally in-depth studies.
Sciences and Engineering
Dissertations in the fields of physics, chemistry, engineering, and biology are often data-heavy, requiring detailed explanations of methodologies and results. However, they tend to be more concise in their literature reviews and theoretical discussions. As a result, the average length for dissertations in these disciplines is generally between 100 to 300 pages.
Business and Management
In business and management, dissertations can vary widely in length due to the diverse nature of research topics, which can range from case studies of specific companies to broad surveys of business trends. Empirical research is common, and the need for practical application often shapes the structure and length. Typically, these dissertations fall between 150 to 250 pages.
Arts and Design
Dissertations in arts and design often combine practical and theoretical research. For instance, a dissertation might include both a written component and a portfolio of artworks or designs. The written portion can range from 100 to 300 pages, and when supplementary material like portfolios or exhibits is considered, the overall “length” can be pretty substantial.
Based on a review of standard dissertations across various key fields, the average page count for a dissertation is approximately 225 pages.
Medicine and Health Sciences
Medical and health sciences dissertations often involve empirical research, such as clinical trials or epidemiological studies. These require detailed methodologies, data presentation, and analysis, making them quite extensive. The average length is often between 150 to 350 pages, not including appendices like data tables or supplementary material.
Law
Legal dissertations often involve a mix of case law analysis, theoretical discussion, and policy implications. They require a deep understanding of legal principles and precedents, making them comprehensive and detailed. The average length for law dissertations is usually between 150 to 300 pages.
Education
Dissertations in education often focus on empirical research, analyzing educational methods, policies, or trends. They require a balance of literature review, data collection, and analysis, making them moderately extensive. The typical length ranges from 150 to 250 pages.
While these figures offer a general guideline, it’s important to remember that the quality of your research and argument is more important than hitting a specific page count. It is strongly recommended to consult your supervisor and adhere to your institution’s guidelines when determining the appropriate length for your dissertation.
Breaking Down the Components of a Dissertation
Now that we know the differences between the sizes of various types and subjects of dissertations, it is also essential to get an idea of the components of the dissertation and how each contributes to the overall length. From the abstract to the reference list, each section has its own set of requirements and formatting guidelines, which can influence the total number of pages.
- Abstract: The abstract is a concise summary of your dissertation, usually not exceeding 300 words. While it’s a small part of the dissertation, it’s critical, providing readers with an overview of what to expect.
- Introduction:The introduction sets the stage for your research, outlining the problem statement, objectives, and research questions. Depending on the complexity of your topic and the need for background information, the introduction can range from 10 to 30 pages.
- Literature Review: This is often one of the lengthier sections, especially for humanities and social sciences dissertations. A thorough literature review can easily span 40 to 100 pages, depending on the breadth of existing research and the number of sources reviewed.
- Methodology: The methodology outlines the research design and, data collection and analysis methods. For empirical dissertations, this section can be quite detailed and lengthy, often ranging from 20 to 50 pages.
- Data Analysis: The heart of any empirical dissertation, this section presents your findings. The length can vary widely based on the volume and complexity of the data, but it’s not uncommon for this section to be 50 to 100 pages.
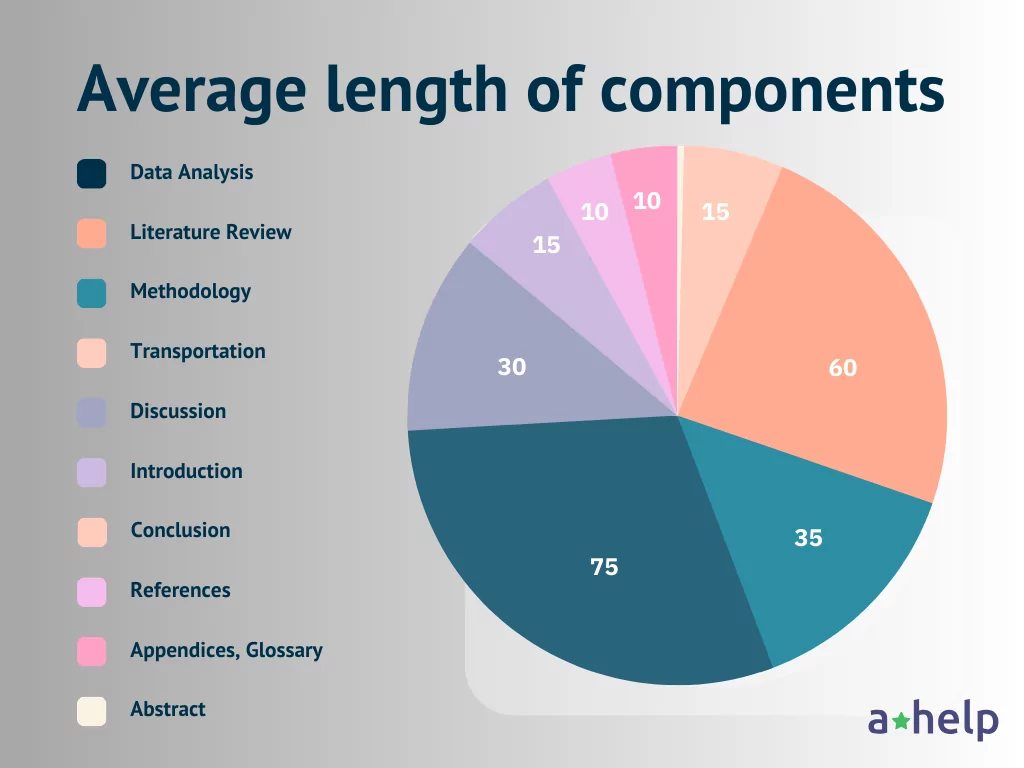
- Discussion: Here, you interpret your findings, linking them to your research questions and the existing literature. This section can range from 20 to 40 pages, depending on the depth of your analysis and the complexity of your argument.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes your research and its implications. It’s usually shorter than other sections, often around 10 to 20 pages.
- References: The reference list can be extensive, especially for dissertations that require a comprehensive literature review. The length can range from 10 to 30 pages.
- Appendices, Glossary, and Other Sections: These are optional and depend on the specific requirements of your discipline or institution. They can include data tables, supplementary analyses, a glossary of terms, or a list of abbreviations. These can add anywhere from 10 to 50 pages to your dissertation.
- Acknowledgments and Preface: These are usually brief, often not exceeding a few pages, but they are an important part of the dissertation, offering a space to thank those who have supported your research journey.
How Long Does It Take to Write a Dissertation?
Writing a dissertation is like setting out on a long expedition. The destination is clear, but the duration of the journey can be uncertain. Just as we’ve explored the length of a dissertation in terms of pages, another relevant question comes up: How much time does it take to pen down this magnum opus of academic achievement?
The time taken to write a dissertation is as varied as the topics they cover. While some scholars might write their work for a couple of years, others, such as professional custom thesis writers, may complete the project in just a few months. Based on general academic standards and practices, we can provide a rough estimate:
Master’s Dissertation: Typically, students take between 6 months to a year to complete a master’s dissertation. This timeframe includes the initial research proposal stage, data collection (if applicable), writing, and revisions.
PhD Dissertation: It is a more extensive piece of work and generally takes 2 to 4 years to complete. This duration encompasses the entire process, from topic selection, extensive literature review, methodology design, data collection, analysis, writing, and multiple rounds of revisions. Some complex empirical studies or projects in disciplines that require extensive fieldwork might even take longer.
Multiple factors influence this variability, each playing a crucial role in determining the pace of progress.
| Nature of the Research | Empirical studies, which require data collection, might take longer due to the time needed for experiments, surveys, or fieldwork. In contrast, theoretical or literature-based dissertations might be quicker to compile but can also be time-consuming due to the depth of analysis required. |
| Academic Discipline | Some fields, like the hard sciences, require extensive lab work, while humanities might demand exhaustive literature reviews. Each discipline brings its own set of time demands. |
| Access to Resources | The availability of necessary resources, such as research materials, lab equipment, or archival documents, can significantly influence the pace. Delays in accessing crucial data or materials can extend the writing process. |
| Supervisory Feedback | The frequency and depth of feedback from your supervisor can influence the pace. Regular, constructive feedback can streamline the process while waiting for inputs or making extensive revisions can add to the timeline. |
| Personal Commitments | Life outside of academia doesn’t pause. Personal commitments, health, family, or even employment can influence the time you dedicate to your dissertation daily. |
| Writing Habits | Everyone has their writing rhythm. Some prefer the slow and steady approach, writing a little daily, while others might have intense bursts of productivity. Understanding and harnessing your personal writing habits can influence the pace. |
While understanding the factors that influence the pace can help in planning, it’s essential to remember that each dissertation has its own rhythm. Embrace the process, seek support when needed, and celebrate each milestone, knowing that the journey, though long, is a significant part of the academic adventure.
FAQ
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.





Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.