
✅ AI Essay Writer ✅ AI Detector ✅ Plagchecker ✅ Paraphraser
✅ Summarizer ✅ Citation Generator
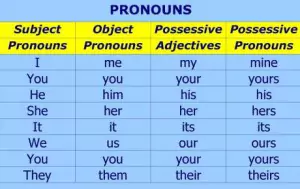
Types of Pronouns
Subjective pronouns
Pronouns that are the subject of a sentence are called subjective pronouns. They can be used to rename the subject (in this case, they follow the verb “to be.”)
e.g. I, he, she, you, they, we
Possessive pronouns
Pronouns that indicate ownership are called possessive pronouns.
e.g. my, their, his, our
Objective pronouns
All other pronouns that are not related to subjective or possessive are objective pronouns.
e.g. me, us, him, her, them
Key Points to Consider
– Pronouns should be agreed in number. For example, German possessive pronouns can be tricky though.Remember that everybody, everything, each, anybody, anyone, anything, either, nobody, neither, no one, someone, something are singular pronouns.
– Try to avoid piling up pronouns. Instead of saying: “Anna has invited him and me to her office,” it would be better to say, “Anna invited us to her office.”
– In sentences with several pronouns, make sure it is clear which noun a pronoun refers to. For example, the sentence, “John and Thomas visited his brother in the hospital,” is troublesome because it is not quite clear whether his is related to John or Thomas.
– Sometimes it is better to change or eliminate a pronoun to make a sentence clearer.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.


Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Comments are closed.